Prostatitis - inflammation of the prostate gland (prostate), a body that produces a liquid secretion that is part of semen. Pathology sometimes causes severe pain and problems with potency. Treatment of prostatitis is reasonable to begin immediately after diagnosis.
Symptoms
Prostatitis typically affects men aged from 25 to 50. Pathology is very common. From it suffers from one-third to half of all the men on the planet. The problem many symptoms:
- one feels discomfort, pain when urinating;
- urine is slow, thin stream, it is necessary to squeeze out;
- at night and at other times of the day there is often a desire to urinate. Can't shake the feeling that not all urine has left the bladder;
- the urine is cloudy, containing blood;
- pestering pain in the lower abdomen, back, groin, perineum (between the scrotum and the anus);
- also haunted by the pain and discomfort in the area of testicles, penis;
- ejaculation occurs with the pain;
There are often symptoms of prostatitis, which is similar to a cold (slight fever, a fever). They are inherent to a bacterial species pathology (more on that below).
Reasons
Prostatitis often occurs in men who previously suffered the disease. The problem gives rise to:
- infection in the bladder and urethra;
- HIV and other diseases that the infected person during sex;
- trauma to the pelvis - falling from bicycles, horses;
Causes of prostatitis in men the catheter in the urethra to drain urine from the bladder.
Pathology sometimes appears after prostate biopsy when the analysis is taken a sample of her tissue. After this procedure, symptoms of prostatitis in men are rare.
Complications
Because prostatitis can:
- to inflame the epididymis (epididymitis);
- greatly decrease sperm count, infertility can ensue;
- appear abscess (cavity with pus).

Many research scientists find no direct link between prostatitis and prostate cancer.
Types of prostatitis
In prostatitis 5 main types: chronic and acute non-bacterial, chronic bacterial, asymptomatic.
- Chronic non-bacterial (also known as chronic pain syndrome in the pelvic region). The most common (more than 90% of all patients hurts it to them). Symptoms of prostatitis are unstable, come and go. Pathogens in the body is not provided. The diagnosis is made if at least 3 months, a person suffers from pain in the pelvic region, discomfort during urination and the other aforementioned symptoms. The exact cause of the disease is unknown, but presumably it is called:
- neurological problems (neuropathy);
- irritation of the prostate, which leads to poor outflow of urine from the bladder;
- problems with the pelvic floor muscles (dyssynergia);
- atypical, yet unknown to science viruses and bacteria.
- Acute non-bacterial. There is a chronic pain syndrome in the pelvic region, permanent problems with urination.
- Acute infectious. The most serious form of the disease. Uncommon. Generated:
- Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus and other bacteria;
- sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, gonorrhea);
- by the fungus Candida.
- Chronic infectious. Pathology may not be evident for several years. The symptoms are similar to acute bacterial type, but are not so much.
- Asymptomatic. It turns out by accident. Symptoms are absent. Ultrasound shows signs of inflammation, and the blood has high concentration prostatospecific antigen.
Symptoms increase quickly. Discomfort in the pelvis joins the soreness of the genitals, fever, nausea, burning pain when urinating. Acute bacterial prostatitis can cause severe, life-threatening complications - abscesses, inability to empty the bladder, low blood pressure.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made by:
- digital rectal examination;
- urine test. Needed to determine whether prostate gland infection;
- blood. Check the level of the prostatospecific antigen. Test reveals signs of inflammation;
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary system. Is assigned when the above tests for an accurate diagnosis is not enough. Ultrasound of the prostate is best done through the anus (transrectally method).
Also sometimes the doctor examines the prostate secretion. To get, a massage of the gland.
May be assigned analyses in various venerologic infections that are the cause of inflammation of the prostate.
A professional diagnosis will help to prescribe the correct treatment of prostatitis in men.
Treatment
If bacterial prostatitis, a doctor prescribes:
- Antibiotics. Their appearance depends on the identified bacteria. Meds would take a month and a half. If the symptoms are very severe, urgent antibiotics are administered intravenously.
- Alpha-blockers. Tools relax the muscles of the bladder in the place where it joins the prostate. Removed pain during urination.
- Analgesics - nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
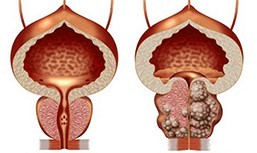
It is impossible to prescribe drugs independently. Only a doctor determines how to treat prostatitis.
Prevention
To prevent prostatitis:
- take a warm sitz bath;
- applied to lower abdomen or back warmer-a pillow;
- stop drinking alcohol, caffeine, food that increases the acidity (spicy, salty);
- consume lots of liquids (unsweetened). So we flush the urinary system, bacteria will not have time to multiply;
- will try for a long time not to ride a bike for a long time not to sit;
- do not forget about the hygiene of the penis, perineum;
- use condoms;
- sports. Simple cardio exercises will be enough - starting to jog, to swim in the pool, do a light workout.
Prevention of prostatitis should be part of the lifestyle. Simple ways to protect the body.































